Table Of Content

In Morse’s notation system, the core component is written in capitals and the supplemental component is written in lowercase letters. For example, in a QUAL → quan design, more weight is attached to the data coming from the core qualitative component. Due to the decisive character of the core component, the core component must be able to stand on its own, and should be implemented rigorously. The key point of this section is for the researcher to begin a study with at least one research question and then carefully consider what the purposes for mixing are. One can use mixed methods to examine different aspects of a single research question, or one can use separate but related qualitative and quantitative research questions.
2 Data collection
In addition, different health service providers and managers can use the results of these assessments to improve the quality of obstetric telephone triage. With this background in mind, the present study aimed to develop an obstetric telephone triage guideline. Clarifying the dimensions and characteristics of obstetric telephone triage is important in improving the quality of services in the health system because researchers can evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, care and diagnostic measures in the form of obstetric telephone triage by developing a guideline.
Data availability
When participants are first offered Miracle Money, the Miracle Messages staff discusses benefits and encourages participants to discuss the topic with a case manager; referrals to financial coaching are also offered. Participants are told that they can use the money in any way they choose but that the program requests the money not be used for any illicit purposes. Of 760 unhoused individuals enrolled in the study, 256 were randomized to receive Miracle Friends, 267 were randomized to receive Miracle Money, and 237 were randomized to the waitlist control group. In the two intervention groups, 360 of 523 unhoused individuals were initially matched to a phone buddy. Of the 191 study participants in the Miracle Money group who had been initially matched to a volunteer phone buddy, 103 were deemed to be participating in the program and began receiving monthly income.
Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review
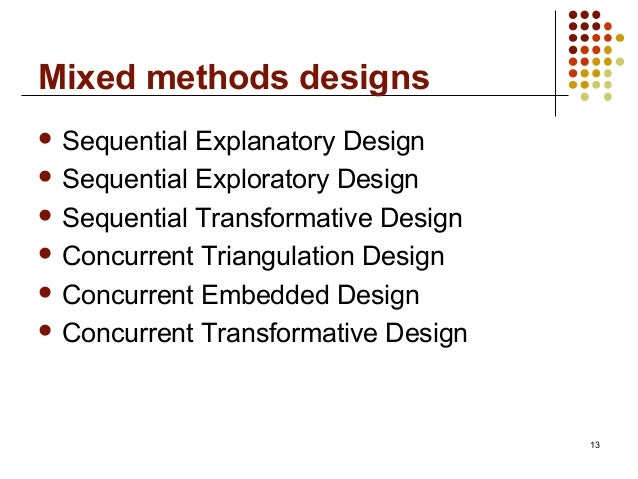
At each stage, one approach affects the formulation of the other, and multiple types of implementation processes can occur. A first set of strategies takes the detected divergence as the starting point for further analysis, with the aim to resolve the divergence. One can also look for a more comprehensive theory, which is able to account for both the results of the first component and the deviating results of the second component. At some point in writing down the results of the first component, the results of the second component are added and integrated. A joint display (listing the qualitative and quantitative findings and an integrative statement) might be used to facilitate this process. Simultaneity (“Simultanität”) forms the basis of the distinction between concurrent and sequential designs.
MedMinas project: design and use of mixed methods in the evaluation of pharmaceutical services in primary health ... - BMC Medical Research Methodology
MedMinas project: design and use of mixed methods in the evaluation of pharmaceutical services in primary health ....
Posted: Sun, 27 Mar 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The design of an Obstetric Telephone Triage Guideline (OTTG): a mixed method study
The issuance and redemption increased and stabilized over the next 3 months of the $24/child/month policy, as illustrated. Despite the strengths of mixed-methods research but there is not much of it in nursing and other fields [7]. A recent review paper shows that the prevalence of mixed-methods studies in nursing was only 1.9% [7]. Similarly, a systematic review synthesised a total of 20 papers [16], and 16 papers [17] on nursing-related research paper among these only one mixed-methods paper was identified. Worse, a further two mixed-methods review recently revealed that out of 48 [18,19] synthesised nursing research papers, not one single mixed-methods paper was identified. This clearly depicts that mixed-methods research is still in its infancy stage in nursing but we can say there is huge scope to implement it to understand research questions on both sides of coin [4].
For example, a survey questionnaire will include a limited number of structured questions, adding qualitative methods can capture other unanticipated facets of the topic that may be relevant to the research problem and help in the interpretation of the quantitative data. A good example of a mixed-methods study, it one conducted in Australia to understand the nursing care in public hospitals and also explore what factors influence adherence to nursing care [14]. Another example is a mixed-methods study that explores the relationship between nursing care practices and patient satisfaction. This study started with a quantitative survey to understand the general nursing services followed by qualitative interviews. A logistic regression analysis was performed to quantify the associations between general nursing practice variables supplemented with a thematic analysis of the interviews [15].
It can answer complex research queries that cannot be solved with either qualitative or quantitative research. In maternal care, developing valid obstetric triage guidelines is critical [48, 49], and that also requires training packages [50]. If providers fail to follow the guidelines or standards, difficulties in fulfilling responsibilities and risks for clients may occur [52]. The guidelines allow all triage personnel to quickly evaluate and provide services to clients.
Full Article - Society of Behavioral Medicine
Full Article.
Posted: Thu, 27 Jun 2019 19:04:22 GMT [source]
Sample Mixed Methods Research Study
Thus, the change in household CVB benefits due to the second policy change would depend on the composition of participants in the household. However, the administrative data contains redemption rates for all participating households in a State, and it is not possible to isolate the redemption rates for children. To best identify the influence of an increase in CVB benefits on redemption rates we limit our ITS to $35/child/month and use PROC SURVEYREG to explore the relationship between CVB issuance and redemption during the entire observation period. Disparities were observed when analyzing both the quantitative and qualitative data by race and ethnicity. Disparities in redemption rates existed prior to the COVID-19 CVB changes with a 2015 study of Virginia WIC participants reporting that the lowest FV redemption rates were among African American and Black participants (35). Implementation of policy changes, such as the changes to the CVB amounts, should incorporate equity-focused strategies (35, 36) to help resolve the barriers to and inequities of CVB redemptions.
Access this chapter
Henwood, Stein, Corletto, and Suthar had full access to all recruitment data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data presentation. Matching of unhoused individuals and volunteers has been primarily based on preferences and shared interests, as indicated on the enrollment application. Once a match is determined, volunteers receive the phone number of their assigned unhoused friend and are asked to make contact as soon as possible. The program has no time limit, and the development of friendships is expected to occur naturally over time and be unique to each matched pair. Volunteers are encouraged to provide a friendly voice and be a compassionate listener without judgment; there is no expectation of formal counseling or case management. If a lack of fit occurs or communication is not maintained between the two individuals, the program offers to rematch the unhoused individual, volunteer, or both.
The selections that Leech and Creswell make regarding the key actors are based on their close involvement with the “MMR movement.” It is corroborated by a simple analysis of the articles that appeared in the Journal of Mixed Methods Research (JMMR), founded in 2007 as an outlet for MMR. (4) using a framework (theoretical or program) to bind together the data sets (Creswell and Plano Clark 2011, p. 76). There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data. By following a thread, the researcher can explore various research topics related to the original issue and gain a more comprehensive view of the issue. Quantitative data is collected through the use of surveys and experiments, for example, containing numerical measures such as ages, scores, and percentages.
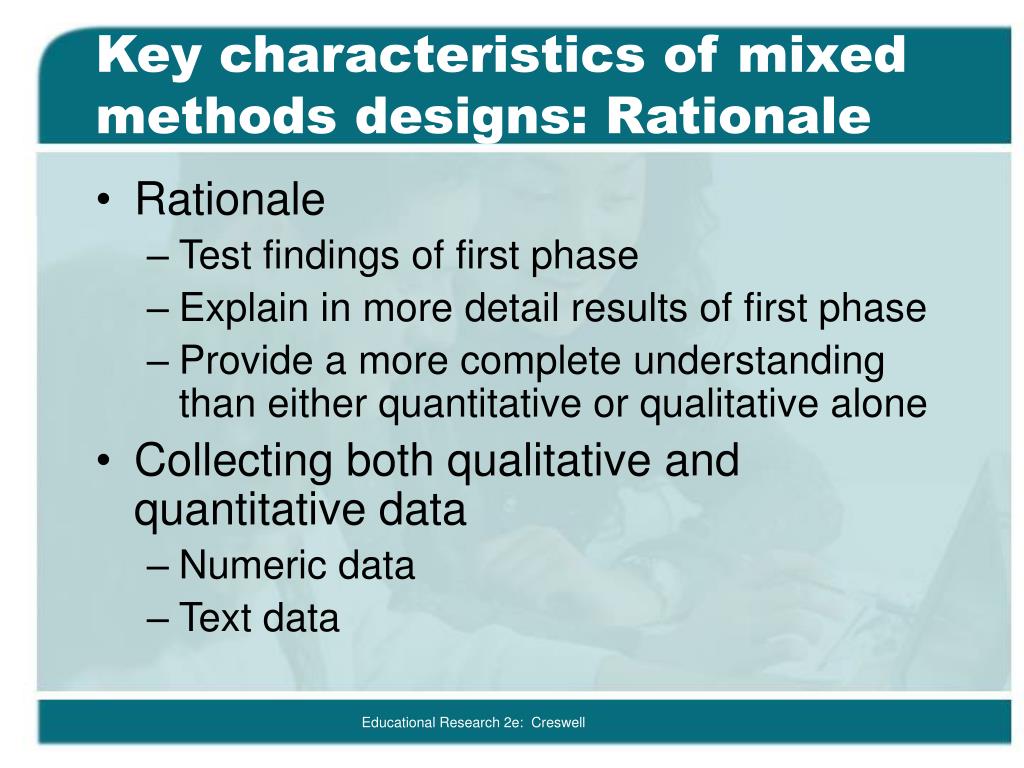
Mixed methods is not simply having quantitative and qualitative data available or analyzing and presenting data findings separately. The integration process can occur during data collection, analysis, or in the presentation of results. According to the National Institutes of Health, mixed methods strategically integrates or combines rigorous quantitative and qualitative research methods to draw on the strengths of each. The second dimension is theoretical drive in the sense that Morse and Niehaus (2009) use this term. That is, will the study have an inductive or a deductive drive, or, we added, a combination of these. Related to this idea is whether one will conduct a qualitatively driven, a quantitatively driven, or an equal-status mixed methods study.
Researchers often struggle to put mixed methods research into practice, as it is challenging and can lead to research bias. Although mixed methods research can reveal differences or conflicting results between studies, it can also offer method flexibility. The second theme discussed in a large number of contributions is the role epistemology plays in MMR. In a sense, epistemology provides the lifeblood for MMR in that methods in MMR are mainly seen in epistemological terms. This interpretation of methods is at the core of the knowledge claim of MMR practitioners, i.e., that the mixing of methods means mixing broad, different ways of knowing, which leads to better knowledge of the research object. It is also part of the identity that MMR consciously assumes, and that serves to set it apart from previous, more practical attempts to combine methods.
While the academic field revolves around universities and other degree-granting institutions, the stakes in the scientific field entail the production and valuation of knowledge. Of course, in modern science these fields are closely related, but they do not coincide (Gingras and Gemme 2006). For instance, part of the production of legitimate knowledge takes place outside of universities. The dependence among components, which may or may not be present, has been summarized by Greene (2007). It is seen in the distinction between component designs (“Komponenten-Designs”), in which the components are independent of each other, and integrated designs (“integrierte Designs”), in which the components are interdependent. The key point here is that the Morse notation provides researchers with a powerful language for depicting and communicating the design constructed for a specific research study.
An explicit attempt to chart the early history of MMR is provided by Johnson and Gray (2010). They frame MMR as rooted in the philosophy of science, particularly as a way of thinking about science that has transcended some of the most salient historical oppositions in philosophy. Philosophers like Aristotle and Kant are portrayed as thinkers who sought to integrate opposing stances, forwarding “proto-mixed methods ideas” that exhibited the spirit of MMR (Johnson and Gray 2010, p. 72, p. 86). In this capacity, they (as well as other philosophers like Vico and Montesquieu) are presented as part of MMR providing a philosophical validation of the project by presenting it as a continuation of ideas that have already been voiced by great thinkers in the past. Our investigation of the rise and institutionalization of MMR relies on Bourdieu’s field approach. In fields, agents occupy a position relative to each other based on the differences in the volume and structure of their capital holdings.
Yet, the quantitative results found that redemption rates slightly increased after the initial transition period of implementing the CVB changes. During the WIC State and local agency interviews, respondents indicated that more WIC participants redeemed higher dollar amounts of the CVB after the change to $35/child/month. The WIC participant interviews also demonstrated that caregivers of WIC participants utilized the increased CVB amounts with many noting that they recalled redeeming nearly the entire $35/child/month or $24/child/month. This study used a rapid qualitative analysis (26), characterized by its efficiency, participatory nature, team-based collaborative efforts, and iterative progression until theoretical saturation. The team began by crafting specific codes from interview questions, anchored in the i-PARIHS and I + PSE frameworks. A code matrix, which underwent two rounds of piloting for refinement, was developed to summarize these insights and capture illustrative quotes.